Understanding the Impact of Septic Tank Contamination on Groundwater
 |
| Septic Tank Contamination on Groundwater |
As an environmental scientist and Septic Tank man for over 40 years, I have
always been fascinated by how human activities can impact our natural
resources. In particular, the contamination of groundwater due to septic tank
systems is an issue that demands attention and understanding. Septic tank
contamination occurs when harmful substances from these systems infiltrate the
surrounding soil and eventually make their way into the groundwater supply,
which is a vital source of drinking water for many communities.
In this article, we will explore the
common causes of septic tank contamination and delve into its effects on
groundwater quality. We will also discuss the health risks associated with consuming
contaminated drinking water and highlight the signs and symptoms to look out
for.
Testing and monitoring techniques for
detecting contamination will be examined, along with proper maintenance
practices for septic systems to prevent future incidents.
Furthermore, we will delve into
remediation techniques aimed at restoring contaminated groundwater and shed
light on collaborative efforts being undertaken globally to address this
pressing issue. By understanding the impact of septic tank contamination on
groundwater, we can take proactive measures to safeguard our precious water
resources for generations to come.
Key Takeaways
•
Septic tank contamination can
lead to the infiltration of harmful substances into groundwater, posing risks
to public health and ecosystems.
•
Common causes of septic tank
contamination include improper maintenance, damaged tanks, and inadequate
system design or installation.
•
Contaminants released from
septic tanks include pathogens, nutrients, heavy metals, and organic compounds,
which can cause various health problems.
•
Regular testing, monitoring,
and preventive measures are essential to ensure the safety of drinking water
and maintain clean groundwater supplies.
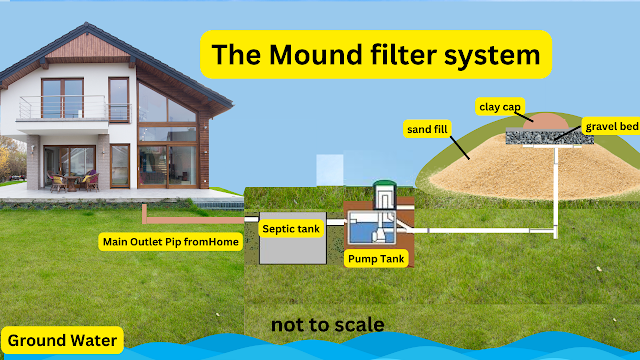
Common
Causes of Septic Tank Contamination
Did you know that one of the main causes of septic tank
contamination is improper maintenance?
Septic tanks are designed to safely treat and dispose of household
wastewater. However, if these systems are not properly maintained, they can
become a major source of groundwater contamination. There are several commoncauses of septic tank contamination that can lead to this problem.
Firstly, lack of regular pumping and cleaning can cause solids to
accumulate in the tank, leading to an increased risk of leakage and overflow.
When solids build up beyond the recommended levels, they can clog the drain
field and prevent proper water filtration. This can result in untreated
wastewater being discharged into the surrounding soil and potentiallycontaminating groundwater.
Secondly, damaged or aging septic tanks can also contribute to
contamination. Cracks or leaks in the tank walls or pipes allow untreated
wastewater to escape into the environment. These leaks may not be immediately
noticeable but can gradually contaminate nearby groundwater sources over time.
Furthermore, inadequate system design or installation can also be
responsible for septic tank contamination. If a system is not correctly sized
for the household's needs or if it is installed too close to wells or surface
water bodies, there is an increased risk of contamination occurring.
Understanding these common causes of septic tank contamination is
crucial in developing effective prevention strategies. By implementing proper
maintenance practices, such as regular pumping and inspections, homeowners can
reduce the risk of contaminating their local groundwater sources.
In the next section, we will explore the effects of septic tank
contamination on groundwater quality without writing 'step'.
Effects
of Septic Tank Contamination on Groundwater Quality
Groundwater quality can be significantly affected by septic tankpollution. When septic tanks aren't properly maintained or functioning, they
can release harmful contaminants into the surrounding soil and water. These
contaminants include pathogens, nutrients, heavy metals, and organic compounds.
All of these have the potential to degrade groundwater quality.
One of the primary effects of septic tank contamination on
groundwater is the presence of bacteria and viruses. Pathogens like E.coli and
giardia can cause serious health risks if ingested through contaminated
drinking water.
Additionally, excessive levels of nitrogen and phosphorus from
septic tanks can lead to nutrient pollution in groundwater. This excess
nutrient concentration promotes the growth of algae and other aquatic plants,
resulting in a phenomenon known as eutrophication. Eutrophication depletes
oxygen levels in water bodies and disrupts aquatic ecosystems.
Furthermore, heavy metals like lead, arsenic, and mercury may also
contaminate groundwater due to improper disposal practices or leaks from
deteriorating septic systems. These heavy metals pose significant health risks
to humans when consumed over time.
Septic tank contamination has a profound impact on groundwater
quality due to the release of various pollutants such as bacteria, viruses,
nutrients, and heavy metals. Understanding these effects is crucial for
implementing effective management strategies to protect our precious
groundwater resources.
The subsequent section will delve into the health risks associated
with contaminated groundwater without writing 'step'.
 |
| Impact of Septic Tank Contamination on Groundwater |
Health
Risks Associated with Contaminated Groundwater
The health risks linked to polluted water sources are truly alarming
and can have devastating consequences. When groundwater becomes contaminated
due to septic tank leakage, it poses serious threats to human health.
Contaminated groundwater often contains harmful pathogens, such as
bacteria, viruses, and parasites, which can cause various diseases when
consumed or even when in contact with the skin. These pathogens can enter the
body through drinking contaminated water or by eating food prepared with it.
One of the most common illnesses associated with contaminated
groundwater is gastrointestinal infection. Pathogens like E.coli and Salmonella
can lead to severe diarrhea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and dehydration. Young
children, pregnant women, elderly individuals, and those with weakened immune
systems are particularly vulnerable to these infections.
In addition to gastrointestinal issues, contaminated groundwater can
also cause respiratory problems. Certain contaminants like nitrates can
contaminate well water and convert into nitrites in the body. In high levels,
nitrites reduce oxygen-carrying capacity in the blood and pose a significant
risk to infants who may develop blue baby syndrome.
Furthermore, exposure to toxic chemicals present in contaminated
groundwater may result in long-term health effects. Substances like heavy
metals (e.g., arsenic), pesticides (e.g., atrazine), and volatile organic
compounds (e.g., benzene) have been linked to cancer development as well as
neurological disorders.
Understanding these potential health risks associated with
contaminated groundwater is crucial for public awareness and policy-making
efforts aimed at preventing septic tank pollution. By identifying signs and
symptoms of contaminated drinking water early on, we can take necessary actions
to safeguard our communities from further harm caused by inadequate sanitation
practices without compromising our access to safe drinking water sources.
Signs and
Symptoms of Contaminated Drinking Water
Exposure to contaminated drinking water can lead to a variety of
health issues, including gastrointestinal infections and respiratory problems.
It's crucial to understand the signs and symptoms of contaminated drinking
water in order to take necessary precautions and protect our health.
One of the most common signs of contaminated drinking water is
gastrointestinal problems such as diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, and stomach
cramps. These symptoms are often caused by bacteria, viruses, or parasites
present in the water.
Additionally, contaminated water may also lead to respiratory
problems like coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath. This can occur when
pollutants such as chemicals or toxins are ingested or inhaled.
Skin irritation is another indicator of contaminated drinking water.
Rashes, itching, or redness on the skin may suggest the presence of harmful
substances in the water supply.
Furthermore, changes in taste, odor, or color can be warning signs
that something is amiss with your drinking water.
It's essential to note that these symptoms may not always be immediately
evident after consuming contaminated water. Some health effects might manifest
gradually over time due to prolonged exposure. Therefore, it's crucial to
monitor any potential changes in your body's responses and seek medical
attention if you suspect contamination.
In order to ensure safe drinking water for everyone, it's vital that
we regularly test and monitor groundwater for contamination. By implementing
comprehensive testing procedures and employing advanced monitoring techniques
like chemical analysis and microbial testing methods across various locations
within a community's water supply system, we can effectively identify any
potential contaminants before they pose a significant risk.
Ensuring continuous monitoring will enable us to maintain high-quality
standards for our groundwater resources while safeguarding public health from
potential hazards associated with septic tank contamination.
Transitioning into the subsequent section about 'testing and
monitoring groundwater for contamination', it becomes evident that regular
assessments play a pivotal role in maintaining clean drinking water supplies
without compromising public health.
Testing
and Monitoring Groundwater for Contamination
To ensure your drinking water is safe, it's important to regularly
test and monitor the quality of groundwater for any potential contaminants.
Testing and monitoring groundwater for contamination is a crucial
step in understanding the impact of septic tank contamination on this valuable
resource. There are several methods that can be used to assess groundwater
quality.
One common method is water sampling, where samples from different
wells or sources are collected and analyzed for various parameters such as pH,
turbidity, and the presence of specific contaminants. This data helps identify
any changes in the groundwater composition over time and provides insight into
potential contamination sources.
Another technique used for monitoring groundwater quality is the
installation of monitoring wells. These wells are specifically designed to
capture water samples from specific depths within an aquifer. By regularly
collecting samples from these wells, scientists can track changes in
contaminant levels over time and determine if there are any trends or patterns.
In addition to regular testing, continuous monitoring systems can also
be installed to measure key parameters such as dissolved oxygen levels,
temperature, conductivity, and pressure. These real-time data provide a more
comprehensive understanding of groundwater dynamics and help detect sudden
changes or anomalies that could indicate contamination events.
By implementing these testing and monitoring strategies, we gain
valuable insights into the quality of our groundwater resources. This
information enables us to make informed decisions regarding preventive measures
for septic tank contamination. It's essential to take proactive steps towards
protecting our precious groundwater supplies by ensuring proper maintenance of
septic systems and adopting best practices for waste management.
Preventive
Measures for Septic Tank Contamination
By taking proactive steps and implementing preventive measures, we
can ensure the long-term health and safety of our valuable groundwater
resources. Septic tank contamination poses a significant threat to the quality
of groundwater, as it can introduce harmful contaminants such as pathogens,
nitrates, and other pollutants. To prevent septic tank contamination from
occurring, it is crucial to follow certain measures.
Firstly, regular pumping and maintenance of septic tanks are
essential. This prevents overloading and ensures proper functioning of the
system. It is recommended that septic tanks be pumped every three to five years
to remove accumulated solids and prevent leakage into the surrounding soil.
In addition to regular pumping, it is important to limit water usage
in households connected to septic systems. Excessive water usage can overwhelm
the tank's capacity and lead to system failure. Implementing water-saving
practices such as fixing leaks promptly, using low-flow fixtures, and avoiding
excessive water use during peak times can help reduce stress on the septic
system.
Proper disposal of household waste is another critical aspect of
preventing septic tank contamination. Avoid flushing non-biodegradable items or
hazardous substances down toilets or drains as they can disrupt the balance
within the tank and potentially contaminate groundwater.
Lastly, maintaining a safe distance between septic systems and
groundwater sources is vital. Ensuring that wells are located uphill from
septic systems minimizes the risk of contamination through downward movement of
pollutants.
By implementing these preventive measures effectively, we can
significantly reduce the likelihood of septic tank contamination impacting our
groundwater resources. Proper maintenance and care of septic systems play a
pivotal role in safeguarding our valuable water supplies for future generations
without compromising their quality or quantity.
Proper
Maintenance and Care of Septic Systems
When it comes to preventing septic tank contamination, there are
several measures that can be taken. However, one of the most crucial aspects is
proper maintenance and care of septic systems. By ensuring regular maintenance,
homeowners can significantly reduce the risk of groundwater contamination.
Proper maintenance involves a series of steps that should be
followed diligently. Firstly, it's essential to have the septic tank pumped
regularly to remove accumulated sludge and scum. This process helps maintain
the optimal functioning capacity of the system and prevents any potential
overflow or leakage. The frequency at which pumping is required depends on
various factors such as household size, water usage, and tank size.
In addition to regular pumping, it's vital to avoid flushing or
disposing of harmful substances into the septic system. Chemicals like
solvents, paints, oils, and medications can disrupt the natural bacterial
balance within the tank and hinder its ability to break down waste properly.
Similarly, excessive use of antibacterial products can also disrupt this
balance.
Furthermore, conserving water usage plays a significant role in
maintaining an efficiently functioning septic system. Reducing water
consumption through practices such as fixing leaks promptly and using
appliances like washing machines and dishwashers efficiently can prevent
overloading the system.
Overall, proper maintenance and care are paramount in preventing
septic tank contamination. By following these guidelines diligently, homeowners
can ensure their systems operate optimally while minimizing groundwater
pollution risks.
As we move forward into discussing regular septic tank inspections
in detail, it becomes evident how important they are in identifying potential
issues before they become major problems for both your septic system and
groundwater quality.
Importance
of Regular Septic Tank Inspections
Regular septic tank inspections are crucial for ensuring the
long-term health and functionality of your home's wastewater treatment system.
These inspections play a vital role in identifying potential issues before they
escalate into costly and damaging problems.
By conducting regular inspections, you can detect any signs of
damage or malfunction early on. This allows for prompt repairs or maintenance,
preventing further deterioration and minimizing the risk of contamination to
groundwater. Inspections also help ensure that the septic tank is operating
efficiently, maximizing its lifespan and reducing the need for premature replacements.
During a septic tank inspection, a professional technician will
assess various components of the system. They will examine the tank itself for
structural integrity, check the inlet and outlet pipes for blockages or leaks,
and evaluate the levels of sludge and scum inside the tank. Additionally, they
may inspect other elements such as pumps, filters, alarms, and drain fields.
These inspections provide valuable data that can be used to identify
potential problems or areas of concern. By analyzing this information,
homeowners can make informed decisions regarding necessary repairs or upgrades
to their septic systems.
Regular septic tank inspections are an essential part of responsible
homeownership. Neglecting these inspections can lead to serious consequences
such as contaminated groundwater and expensive remediation efforts. Therefore,
it's crucial to prioritize routine inspections to ensure proper functioning of
your septic system.
Understanding how regular inspections contribute to maintaining a
healthy wastewater treatment system sets the stage for exploring remediation
techniques for contaminated groundwater without compromising environmental
safety standards.
Remediation
Techniques for Contaminated Groundwater
Implementing effective techniques to address contaminated
groundwater is crucial for preserving the safety and sustainability of our
water resources. When groundwater becomes contaminated due to septic tank
leakage or overflow, it poses a significant threat to public health and the
environment. Therefore, it's essential to employ remediation techniques that
can effectively remove contaminants and restore the quality of the groundwater.
One commonly used technique for remediating contaminated groundwater
is pump-and-treat. This method involves extracting groundwater from affected
areas using wells and pumping it through a treatment system before
reintroducing it back into the aquifer or discharging it safely. The treatment
process typically includes physical filtration, chemical dosing, and biological
degradation, depending on the specific contaminants present in the groundwater.
Another technique that has shown promising results is in-situ
bioremediation. This approach involves stimulating naturally occurring
microorganisms in the subsurface to degrade contaminants directly within their
environment. Various methods can be used to enhance microbial activity, such as
injecting nutrients or oxygen into the contaminated zone. In-situ
bioremediation offers several advantages over traditional remediation methods,
including cost-effectiveness and minimal disturbance to the surrounding
ecosystem.
Additionally, advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) have gained
attention as an innovative solution for treating contaminated groundwater. AOPs
involve generating highly reactive hydroxyl radicals that can break down a wide
range of organic pollutants through oxidation reactions. These processes can
effectively remove persistent organic compounds that are resistant to
conventional treatment methods.
Implementing these remediation techniques plays a vital role in
restoring contaminated groundwater quality and safeguarding our water
resources. By employing pump-and-treat systems, in-situ bioremediation
approaches, or advanced oxidation processes, we can mitigate the adverse
effects of septic tank contamination on our precious water sources. Moving
forward, collaborative efforts among stakeholders will be essential in
addressing septic tank contamination comprehensively without compromising human
health or environmental integrity.
Collaborative
Efforts to Address Septic Tank Contamination
By working together and pooling resources, stakeholders can
effectively combat the issue of septic tank contamination, ensuring the
long-term health and sustainability of our water sources. Collaborative efforts
have emerged as a crucial approach in addressing this problem, as they bring
together various stakeholders such as government agencies, environmental
organizations, and local communities to develop comprehensive strategies for
remediation.
One key aspect of collaborative efforts is education and awareness
campaigns. These initiatives aim to inform the public about the risks
associated with septic tank contamination and promote responsible waste
management practices. By raising awareness about the potential impacts on
groundwater quality, these campaigns empower individuals to take proactive
steps in maintaining their septic systems properly.
Another important component is data collection and analysis. Through
collaborative monitoring programs, stakeholders can gather accurate information
about the extent of contamination and its effects on groundwater quality. This
data-driven approach enables them to identify hotspots where contamination
levels are high and prioritize remediation efforts accordingly.
In addition to education and data-driven approaches, collaboration
also fosters knowledge sharing among stakeholders. By exchanging experiences,
best practices, and lessons learned from previous remediation projects,
stakeholders can optimize their strategies for addressing septic tank
contamination. This collective knowledge contributes to a more efficient
allocation of resources and ensures that interventions are tailored to specific
regional conditions.
Overall, collaborative efforts play a vital role in tackling septic
tank contamination by leveraging diverse expertise and resources. Through
education campaigns, data collection, analysis, and knowledge sharing
initiatives, stakeholders can work towards sustainable solutions that safeguard
our groundwater sources for future generations. It's imperative that we
continue to foster collaboration among all relevant parties to effectively
address this pressing issue.
Frequently Asked
Questions
How often should
I have my septic tank inspected?
You
should have your septic tank inspected every 1-3 years to ensure it is
functioning properly. Regular inspections can help identify potential issues
early on and prevent contamination of groundwater.
What are the
potential long-term health effects of drinking contaminated groundwater?
Drinking
contaminated groundwater can lead to severe health effects in the long term.
These may include gastrointestinal illnesses, kidney damage, liver problems,
and increased risk of certain cancers.
Are there any
natural remedies or treatments available to clean up contaminated groundwater?
There
are natural remedies, such as bioremediation and phytoremediation, that can
help clean up contaminated groundwater. These methods utilize microorganisms or
plants to break down pollutants and restore water quality.
Can septic tank
contamination affect the taste or smell of my drinking water?
Yes,
septic tank contamination can affect the taste and smell of drinking water. The
presence of bacteria, viruses, and other pollutants can lead to unpleasant
odors and flavors in the water supply.
What steps can
individuals take to reduce the risk of septic tank contamination in their area?
To
reduce the risk of septic tank contamination in your area, it's important to
properly maintain and regularly inspect your septic system. This includes
pumping the tank as needed, avoiding excessive water use, and disposing of
waste correctly.
.png)


.png)





Comments
Post a Comment